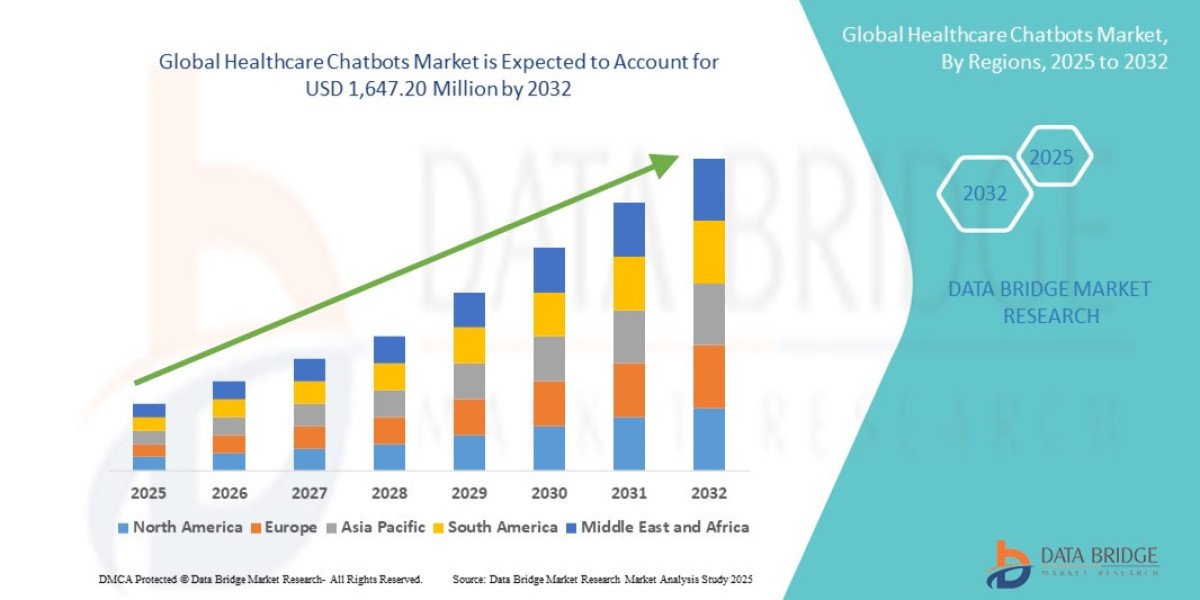
For European entrepreneurs and companies seeking global growth, India stands out as a land of opportunity. With its massive consumer base, expanding middle class, digital transformation, and business-friendly reforms, India has become a preferred destination for foreign investors. Understanding how to start business in India from Europe requires clarity on regulations, strategy, and cultural dynamics. While the distance may seem challenging, modern digital processes and professional support make it entirely feasible to establish and manage an Indian business from Europe.
Why European Entrepreneurs Are Looking Toward India
India’s economic growth, young population, and increasing demand for products and services make it an attractive market. Sectors such as technology, manufacturing, renewable energy, pharmaceuticals, logistics, and e-commerce are experiencing rapid expansion. For European businesses, India offers cost efficiency, access to skilled talent, and the ability to serve both domestic and global markets from one base.
Additionally, India maintains strong trade relations with many European nations and has double taxation avoidance agreements that help reduce tax burdens for foreign investors. These factors collectively make India a strategic choice for long-term business expansion.
Deciding Your Market Entry Strategy
Before registering a company, it is essential to decide how you want to enter the Indian market. Some European entrepreneurs start by exporting goods or services to India to test demand. Others prefer a direct presence through a registered entity to build trust and scale operations faster.
Your entry strategy may include setting up a wholly owned subsidiary, partnering with an Indian company, or establishing a branch office. The right approach depends on your business goals, budget, industry regulations, and desired level of control.
Selecting the Appropriate Legal Entity
Choosing the correct legal structure is a foundational step. The most common options for foreign entrepreneurs include:
A Private Limited Company, which is widely preferred due to limited liability, ease of raising capital, and acceptance by Indian clients and investors.
A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP), which offers operational flexibility and fewer compliance requirements, suitable for consulting and professional services.
A Branch Office, which allows an existing European company to conduct business activities in India without forming a separate legal entity.
A Liaison Office, which is limited to non-commercial activities such as market research and relationship building.
Each structure has different compliance and tax implications, so professional advice is strongly recommended.
Understanding India’s FDI Framework
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) regulations play a critical role in determining what kind of business activities you can undertake. Many sectors allow 100% foreign ownership under the automatic route, meaning no prior government approval is required. However, some industries are regulated and may need approval from Indian authorities.
European entrepreneurs must carefully review sector-specific FDI guidelines to ensure compliance. Failure to follow these rules can result in delays or legal complications later.
Company Registration and Documentation Process
Registering a business in India involves several formal steps. These include obtaining identification numbers for directors, securing digital signatures, and filing incorporation documents with the relevant authorities. You will also need a registered office address in India, which can initially be a virtual or shared office in many cases.
Although the process may appear complex, it can be handled efficiently from Europe with the help of Indian consultants who manage documentation, filings, and approvals on your behalf.
Opening Bank Accounts and Managing Finances
Once the company is registered, opening a corporate bank account in India is mandatory. Banks conduct due diligence, especially for foreign-owned entities, and may require additional documentation under foreign exchange regulations.
From a financial perspective, understanding Indian taxation is essential. This includes corporate tax, goods and services tax (GST), and withholding taxes. Proper accounting systems and tax planning will help you remain compliant and optimize profitability.
Building a Local Team and Infrastructure
India offers access to a vast pool of skilled professionals across industries. You can hire full-time employees, freelancers, or outsource specific functions such as IT, customer support, or digital marketing. Employment laws must be followed, including contracts, minimum wages, and social security contributions.
For European founders managing operations remotely, appointing a trustworthy local manager or partner can ensure smooth day-to-day functioning while you focus on strategy and expansion.
Navigating Cultural and Business Practices
Understanding Indian business culture is just as important as legal compliance. Relationship-building, patience in negotiations, and respect for hierarchy often play a key role in successful partnerships. Decision-making timelines may differ from Europe, and flexibility is essential.
From a market perspective, India is highly diverse. Consumer behavior, pricing expectations, and preferences vary significantly across regions. Conducting local market research and adapting your offerings accordingly can significantly improve your chances of success.
Ensuring Ongoing Compliance and Governance
After incorporation, businesses in India must meet ongoing compliance requirements. These include annual filings, audits, tax returns, and regulatory disclosures. Non-compliance can lead to penalties and impact your company’s reputation.
Working with experienced chartered accountants, legal advisors, and company secretaries can help you stay compliant while reducing administrative burden.
Using Trade Networks and Support Systems
European entrepreneurs can leverage support from embassies, trade councils, startup incubators, and bilateral chambers of commerce. These organizations often provide guidance, networking opportunities, and insights into doing business in India.
Participating in industry events and trade fairs can further help you build connections, identify partners, and gain firsthand knowledge of the Indian market.
Final Word
Learning how to start business in India from Europe is not just about paperwork and regulations; it is about building a sustainable bridge between two dynamic markets. With proper planning, the right legal structure, cultural understanding, and professional support, European entrepreneurs can successfully establish and grow their presence in India. While challenges exist, India’s scale, growth potential, and openness to foreign investment make it a compelling destination for those ready to think long term and act strategically